 Construction – Casing Cutter housings are made of a thick-gauge steel. Casing Cutters must be made very durable to withstand extreme forces while cutting. High quality alloy materials are used. Critical parts are heat treated, including the cutter blade.
Construction – Casing Cutter housings are made of a thick-gauge steel. Casing Cutters must be made very durable to withstand extreme forces while cutting. High quality alloy materials are used. Critical parts are heat treated, including the cutter blade.Sizes – Casing Cutters are made for 6″ to 14″ pipe. Custom sizes for 16″ pipe and larger are also available. So far any size a customer has asked for has been made, including a 28″ Casing Cutter.
FAQ:
Q. How many cutter wheels/blades are in the Casing Cutter?
A. One.
Q. How long will a cutter blade last?
A. Several cuts if you are careful, but sometimes only one.
Q. How do you know if the cutter blade needs to be replaced?
A. Visual inspection, see if the sharp edge is gone.
Q. How long do the Roller Balls last?
A. Longer than the blades, they are hard chrome ball bearings.
Q. How thick of pipe will the Casing Cutter cut?
A. 1/4″ to 3/8″. Also 1/2″ with special tooling.
Q. What thread connector is at the top of the Casing Cutter?
A. 3 1/2″ API pin

Parts List
| Complete Unit - Part # Casing Cutter 6000 | Part Numbers |
|---|---|
| Top Pin Connector | Casing Cutter 6001 |
| Piston | Casing Cutter 6002 |
| Piston Seal | Casing Cutter 6003 |
| Cylinder Top Barrel | Casing Cutter 6004 |
| Main Center Body | Casing Cutter 6005 |
| Roller Ball Retainer Bolt | Casing Cutter 6006 |
| Roller Ball | Casing Cutter 6007 |
| blade Holder Cross Slide | Casing Cutter 6008 |
| Cutter blade | Casing Cutter 6009 |
| Cutter blade Retaining Bolt | Casing Cutter 6010 |
| Spring Can Bottom Barrel | Casing Cutter 6011 |
| Vertical Slide | Casing Cutter 6012 |
| Locking Nut for Stroke Adjustment | Casing Cutter 6013 |
| Stroke Adjustment Bolt | Casing Cutter 6014 |
| Main Spring | Casing Cutter 6015 |
| Bottom Cap | Casing Cutter 6016 |
Assembly – Top
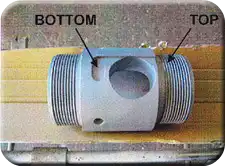
Grease All Threads During Assembly
Main Body #5 – Short groove is on bottom like a capital “L.”

Cylinder Top Barrel #4 has only one end, with thread matching the Main Body #5.
Cylinder Top Barrel #4 is longer than the Bottom Barrel #11.

Make sure Piston Seal #3 is on the piston and the flair side of the seal points to the long side (top) of the brass piston.

Insert Piston #2, with packing at bottom and cup side up.

Piston inserted.

Top Pin Connector #1 completes top assembly.
Assembly – Bottom

Insert Vertical Slide #12 from the bottom
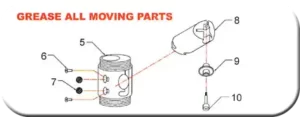
Grease Chart
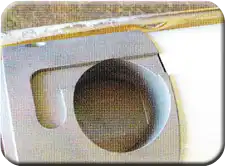
Look into hole opening to see the blade Holder Cross Slide #8.
Rotate the Vertical Slide #12 so the flat spot at the end of the track is centered in the opening.

Insert the blade Holder Cross Slide #8 into the pocket with the slope on the bottom matching the slope of the Vertical Slide #12.

Push the Vertical Slide #12 upward and trap the blade Holder Cross Slide #8 in the T-slot track.

The Stroke Adjustment Bolt #14 is pre-adjusted and locked by the Locking Nut #13 at the factory.
Screwing in the Stroke Adjustment Bolt #14 a little further makes the cutter blade come out a little further.
Assembly – Test and Adjust

These parts should be oiled (Rock Drill oil works well).

Push the slide up and down to make sure it slides easily and the cutter blade goes in and out.
Assembly – Bottom

Screw on the Spring Can Bottom Barrel #11

Insert Main Spring #15.

It may take two strong people to push the spring in and start threading the Bottom Cap #16. To change the blade, unscrew the Bottom Cap far enough to allow the Vertical Slide #12 to be pushed down by air (or by broomstick) allowing the cross slide to be pulled out.
CAUTION: Do not unscrew the Bottom Cap #16 all the way! It could surprise or injure you. The blade Holder Cross Slide #8 can be removed when the bottom cap is half way unscrewed.
Operating Case Cutter
Making a Cut – After the Casing Cutter is placed at the desired depth, begin rotation before turning on the air. Rotation speed should not be over 12 RPM for 6″ pipe and not more than 6 RPM for 12″ pipe.
As air pressure builds, the Casing Cutter will be make its cut through the pipe. The cut is often complete before the air reaches full air pressure, which should be about 200 to 300 PSI. 150 PSI will take perhaps 15 seconds longer.
How do you know when the pipe is cut through? You may see the pipe move or jerk. With thin wall pipe, the cut is usually made in less than one minute. Pipe has been cut in as little as 20 seconds. Thicker wall pipe like 3/8″, consult with a representative.
Retracting the blade – Rotating with the air bled off will push the blade back into the Casing Cutter. Do this before pulling out of the hole.
Storing the Casing Cutter – It is important to remember that the Casing Cutter might be stored long enough to rust, in between uses. You will thank yourself later when you take out a good working tool when you need it.
There are three main areas to grease:
- Roller Ball Retainer Bolt #6
- Roller Boll #7
- blade Holder Cross Slide #8
If you disassemble your Casing Cutter, be sure to grease the threads as you put it back together.
